When people think of heart care, they often picture cardiologists with stethoscopes or high-tech EKG machines. But there’s another professional whose role is just as important in diagnosing and monitoring heart health, the cardiac sonographer.
Cardiac sonographers, sometimes called echocardiographers, use ultrasound technology to produce detailed images of the heart. These images help doctors detect and treat conditions like valve disorders, heart disease, and congenital abnormalities. The work is both highly technical and deeply rewarding, combining science with patient care.
In this guide, we will walk through everything you need to know about the career from cardiac sonographer education and training to salary expectations, career outlook, and how to become a cardiac sonographer.
What Does a Cardiac Sonographer Do?
A cardiac sonographer is responsible for performing echocardiograms, which use high frequency sound waves to create moving images of the heart. These images allow cardiologists to see how the heart functions in real time.
Common duties include:
-
Preparing patients for echocardiography exams
-
Operating ultrasound equipment to capture images of the heart
-
Identifying structural or functional heart issues
-
Assisting cardiologists in diagnosing cardiovascular conditions
-
Maintaining equipment and patient records
Some sonographers specialize further, particularly in pediatric cardiac sonography, where they work with infants and children who have congenital heart conditions.
This career requires not only technical skills but also compassion and communication. Patients may feel anxious during exams, and sonographers play a key role in making them feel comfortable.
Cardiac Sonographer Salary: How Much Can You Earn?
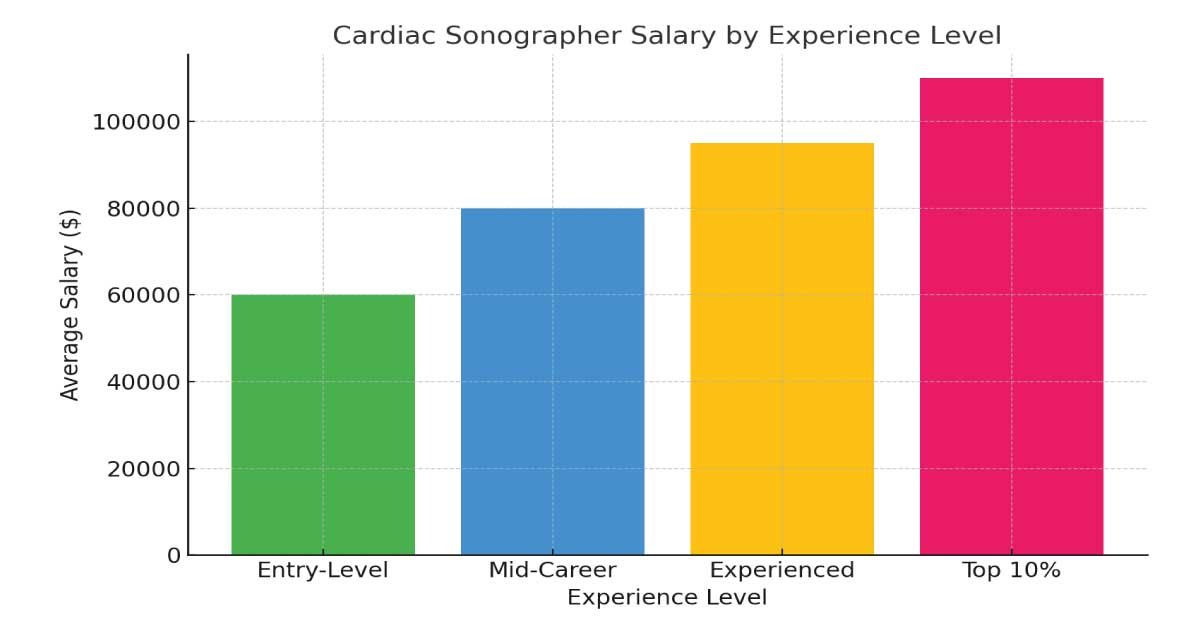
The salary of a cardiac sonographer is one of the biggest attractions to this career. Pay depends on location, education, certification, and experience level.
Average Salary in the U.S.:
Entry-Level: $60,000 – $65,000
Mid-Level: $75,000 – $85,000
Experienced: $90,000 – $95,000+
Pediatric Specialists: Often earn at the higher end due to advanced skills
Salary by Workplace Setting
| Workplace Setting | Average Salary Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Hospitals | $78,000 – $84,000 | Most common employer; steady schedules and career growth |
| Outpatient Diagnostic Centers | $72,000 – $80,000 | Often more regular hours, but slightly lower pay |
| Private Cardiology Practices | $75,000 – $85,000 | Close patient relationships, competitive pay |
| Pediatric Hospitals/Clinics | $85,000 – $95,000+ | Specialized training in pediatric cardiac sonography required |
| Academic/Research Facilities | $70,000 – $78,000 | Opportunities for teaching and contributing to new technologies |
As you can see, salaries vary, but the profession offers both financial security and career stability. With cardiovascular disease on the rise, demand for trained sonographers is expected to grow steadily over the next decade.
❤️ Read This Comprehensive Guide 👉 Entry Level Cardiac Sonographer Salary: Real Pay Insights
Cardiac Sonographer Education and Schooling
Becoming a cardiac sonographer isn’t something you can achieve overnight, it’s a career path that requires both dedication and structured education. A successful sonographer must understand human anatomy, medical terminology, and the science of ultrasound imaging. But just as important is the hands-on training that takes place in hospitals or clinics, where students learn to interact with real patients.
This combination of classroom learning and clinical practice creates a foundation of knowledge and confidence. Whether you are just starting out after high school or already working in healthcare and looking to specialize, there are multiple ways to enter the field. Let’s break down the education pathways and explore the best options.
Education Pathways
Cardiac Sonographer Degree
For most students, the journey begins with a degree. The two main options are:
Associate Degree in Cardiovascular Sonography: This is the fastest route, typically taking two years to complete. It covers the core areas of cardiac sonographer education, including anatomy, ultrasound principles, and echocardiography techniques. An associate degree prepares you for entry-level roles and certification exams.
Bachelor’s Degree in Diagnostic Medical Sonography: A four-year program that goes deeper into advanced imaging, patient care, and research methods. Students who choose a bachelor’s degree often gain more clinical experience and may be eligible for leadership positions later in their career.
While both degrees can lead to a rewarding career, a bachelor’s degree often opens doors to management, teaching, and advanced specialties such as pediatric cardiac sonography.
Cardiac Sonographer Certification Programs
Once you finish your degree, the next step is certification. Most employers won’t hire you unless you’ve proven your skills through a recognized exam.
Two of the most common certifications are:
Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer (RDCS) – Offered by ARDMS
Registered Cardiac Sonographer (RCS) – Offered by CCI
These exams test your ability to perform echocardiograms, interpret images, and apply knowledge of cardiovascular anatomy. Completing cardiac sonographer certification programs is the best way to prepare, as they are designed specifically to help students meet exam requirements.
Certification is more than just a formality. It demonstrates to employers and patients that you’re committed to quality and safety. It also increases your career options and salary potential.
Pediatric Cardiac Sonographer Schooling
If you have a passion for working with children, you may want to specialize in pediatric care. Pediatric cardiac sonographer schooling goes beyond standard training and focuses on the unique challenges of imaging infants and young patients.
This specialization requires:
-
Advanced coursework in congenital heart defects
-
Training on specialized pediatric ultrasound equipment
-
Clinical rotations in children’s hospitals or pediatric cardiology clinics
Since children’s hearts are smaller and often have different medical conditions compared to adults, pediatric cardiac sonographers need extra precision and knowledge. Completing this training can also boost your earning potential, as specialists are in high demand.
Cardiac Sonography Programs: Choosing the Right Path
Not all cardiac sonography programs are created equal, and choosing the right one can make a huge difference in your career. Beyond tuition costs and location, students should consider program quality, accreditation, and clinical partnerships.
Options for Students
Cardiac Sonography Accredited Programs
Accreditation is crucial. Look for schools accredited by CAAHEP (Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs). Accredited programs meet national standards and ensure you’re eligible for certification exams after graduation.Cardiac Sonographer Course Certificates
These shorter programs are designed for those who already have a healthcare background, such as nurses or radiology technicians, who want to transition into cardiovascular sonography. They focus on echocardiography and can be completed in less time than a degree.Cardiac Sonography Classes
Classes include a mix of theory and practice, covering ultrasound physics, cardiovascular anatomy, and patient care skills. Clinical practice, where you perform supervised scans, is essential to becoming job-ready.Online Cardiac Sonography Programs
For students who need flexibility, online cardiac sonography programs are a great option. You can complete lectures and coursework online, but remember that clinical training must still be done in person at an approved site.Best Cardiac Sonography Schools
The best schools often partner with hospitals or diagnostic centers, giving students opportunities to apply what they learn in real-world settings. They also have strong student support, career services, and high certification exam pass rates.
The Importance of Certification
Certification is the final step before officially working as a sonographer. Employers value certified professionals because it ensures they can trust your skills and knowledge.
Common Certifications
Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer (RDCS) – The most widely recognized credential in cardiac imaging.
Registered Cardiac Sonographer (RCS) – Another respected certification for those in cardiac sonography accredited programs.
Benefits of Certification
Higher Salary Potential – Certified sonographers often earn several thousand dollars more per year compared to uncertified peers.
Better Job Security – Hospitals and clinics prefer certified staff, especially for specialized areas like pediatric cardiac sonography.
Career Advancement – Certification is often required for leadership, teaching, or research positions.
Professional Credibility – Patients and physicians trust certified sonographers to deliver accurate, high-quality results.
Completing cardiac sonographer certification programs is the best way to prepare. These programs provide focused training, practice exams, and clinical skills to ensure you succeed.
How to Become a Cardiac Sonographer: Step-by-Step
If you are interested in entering the healthcare field and want a career that combines technology, patient care, and strong job growth, becoming a cardiac sonographer could be the right choice for you. This path requires dedication, the right education, and a willingness to keep learning throughout your career. Below is a detailed roadmap that explains each stage in the process.
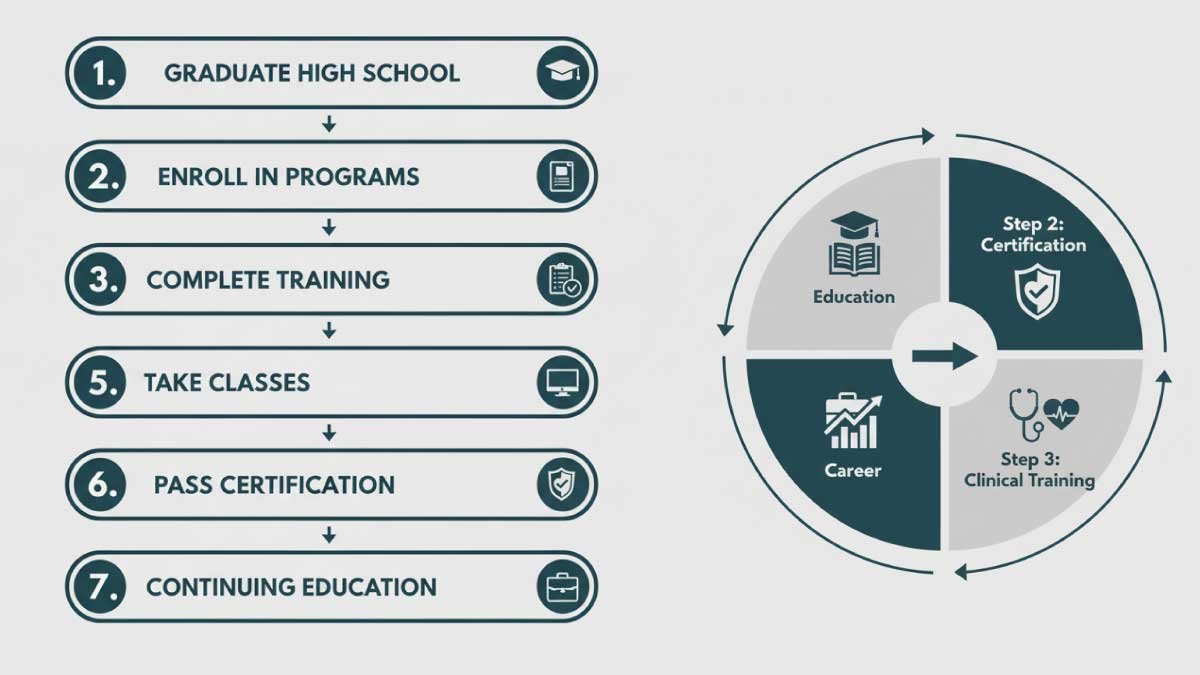
Step 1: Graduate High School or Equivalent
Every journey begins with the basics. To become a cardiac sonographer, you will need at least a high school diploma or GED. While in high school, it’s smart to focus on courses that will build a solid foundation for your future studies.
Math and Physics: These help you understand ultrasound technology and sound wave principles.
Biology and Chemistry: These prepare you for anatomy, physiology, and medical sciences.
Computer Science: Useful because cardiac sonography relies heavily on operating advanced imaging equipment.
Students who excel in science classes often find the transition into cardiac sonography programs much smoother. If you are still in high school, consider volunteering in hospitals or clinics to get exposure to healthcare environments.
Step 2: Enroll in Cardiac Sonography Programs
Once you’ve completed high school, the next step is formal education. There are multiple cardiac sonography programs available, and your choice depends on your long-term goals.
Associate Degree in Cardiovascular Sonography: Takes about two years and is the fastest route to entry-level employment.
Bachelor’s Degree in Diagnostic Medical Sonography: A four-year program offering broader knowledge, research opportunities, and pathways to leadership.
Cardiac Sonographer Course Certificates: Shorter options designed for healthcare professionals transitioning into cardiovascular sonography.
No matter which path you choose, make sure the program is accredited. Cardiac sonography accredited programs ensure you’re eligible to sit for certification exams after graduation.
Step 3: Complete Cardiac Sonographer Training
Classroom learning is important, but this career is highly practical. Cardiac sonographer training involves hands-on practice through clinical rotations. During these rotations, students work in real healthcare facilities under supervision.
Here you’ll learn how to:
-
Operate ultrasound machines effectively
-
Position patients for accurate imaging
-
Handle nervous or high-risk patients with compassion
-
Collaborate with cardiologists and other medical staff
This training builds the confidence and skills you need to step into your first job without hesitation.
Step 4: Take Cardiac Sonography Classes
While training focuses on application, classroom learning builds your knowledge base. Core cardiac sonography classes include:
-
Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart
-
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology
-
Ultrasound Physics and Instrumentation
-
Echocardiography Techniques
-
Patient Care and Medical Ethics
These classes ensure you understand both the science behind ultrasound and the clinical importance of each image you capture.
Step 5: Pass Certification Exams
After completing your education and clinical requirements, the next major milestone is certification. Most employers require you to be certified before hiring you.
Two widely recognized certifications include:
RDCS (Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer) – Offered by ARDMS
RCS (Registered Cardiac Sonographer) – Offered by CCI
Certification shows that you have met national standards in knowledge and skill. Completing cardiac sonographer certification programs is the best way to prepare for these exams.
Step 6: Apply for Jobs in Various Settings
With certification in hand, you are ready to begin your career. Cardiac sonographers are in demand in a variety of environments:
Hospitals – The largest employer of cardiac sonographers, offering stable shifts and growth potential.
Outpatient Diagnostic Centers – Provide more routine hours, often without overnight shifts.
Private Cardiology Practices – Allow for close patient relationships.
Pediatric Hospitals or Clinics – Require specialized training in pediatric cardiac sonography, focusing on infants and children with congenital heart conditions.
Step 7: Pursue Continuing Education
The world of healthcare is always evolving, and so is the field of sonography. Once you start working, it’s important to continue learning through workshops, advanced certifications, or even a cardiac sonographer degree at the bachelor’s level.
This is especially true for those in pediatric cardiac sonography, where technology and treatment approaches are constantly advancing. Continuing education ensures you stay competitive and deliver the best possible patient care.
Career Growth and Opportunities
The field of cardiovascular sonography is not only stable but also offers excellent growth opportunities. As you gain experience, you can move into specialized or leadership positions.
Possible Career Paths:
Lead Sonographer/Supervisor – Manage teams and oversee imaging operations.
Educator – Teach in cardiac sonography accredited programs and help train the next generation of sonographers.
Pediatric Cardiac Sonographer – Provide specialized care for children, a growing subspecialty with high demand.
Research and Development – Collaborate with equipment manufacturers to advance ultrasound technology.
With cardiovascular disease being one of the most common health challenges globally, demand for sonographers is projected to grow much faster than the average occupation. This means consistent job opportunities and job security well into the future.
Why Choose Cardiac Sonography as a Career?
Beyond the technical skills and strong job outlook, this career offers something more meaningful: the chance to impact lives every single day.
Top Benefits of Becoming a Cardiac Sonographer:
Strong Salary Potential – With many earning between $70,000 and $95,000 annually.
Job Stability – Cardiovascular imaging is essential in nearly every hospital and clinic.
Diverse Work Environments – Opportunities range from large hospitals to small private practices.
Specialization Opportunities – Focus on areas like adult echocardiography or pediatric cardiac sonography.
Personal Fulfillment – Knowing your work helps diagnose and save lives is incredibly rewarding.
Choosing this path is not just about a paycheck, it’s about joining a career where science and compassion meet to improve patient outcomes.
Final Thoughts
A cardiac sonographer is more than just a technician, they are a key player in the fight against heart disease. From capturing vital images to working alongside cardiologists, their role is essential in modern healthcare.
With strong salaries, a positive career outlook, and opportunities for specialization, it’s no wonder many students are drawn to this field. By enrolling in cardiac sonography programs, pursuing cardiac sonographer certification, and considering the best cardiac sonography schools, you can confidently step into a career filled with purpose, stability, and growth.
If you are passionate about healthcare and technology, the path to become a cardiac sonographer may be the perfect fit for you.
💚 👉 Want to explore how much sonographers earn across the United States? Visit Sonographer Salary for accurate insights. Learn hourly, monthly, and yearly wages by specialization, experience, and location with complete salary breakdowns and reliable data for professionals.
FAQs:
Is being a cardiac sonographer hard?
Yes, becoming a cardiac sonographer can be challenging, but it’s highly rewarding. The field requires strong knowledge of anatomy, ultrasound physics, and cardiovascular conditions. Clinical training can be intense since you work directly with patients under supervision. However, if you enjoy healthcare and technology, the learning curve feels exciting. With dedication, many students find the mix of science, patient care, and hands-on practice both manageable and fulfilling.
How long does it take to become a cardiac sonographer?
Most people take 2 to 4 years to become a cardiac sonographer. An associate degree in cardiovascular sonography takes about two years, while a bachelor’s degree may take four. Some already licensed healthcare professionals complete certificate programs in 12–18 months. Time also includes clinical rotations and preparing for certification exams like RDCS or RCS. The exact timeline depends on the program path and prior education.
Do cardiac sonographers make good money?
Yes, cardiac sonographers earn excellent salaries compared to many allied health careers. Entry-level pay is around $60,000 to $65,000 annually, while mid-level professionals often earn $75,000–$85,000. Experienced sonographers or those working in pediatric cardiac sonography can earn $90,000–$95,000+. Salaries may also increase in urban areas or teaching hospitals. Certification, advanced education, and years of experience all contribute to boosting income and long-term financial growth.
What’s the difference between a cardiac sonographer and an ultrasound technician?
An ultrasound technician is a general term describing professionals who perform imaging on different parts of the body, like the abdomen, obstetrics, or vascular systems. A cardiac sonographer, however, specializes in imaging the heart through echocardiography. Their training focuses on cardiovascular anatomy, heart diseases, and advanced ultrasound techniques specific to cardiac care. This specialization makes cardiac sonographers highly skilled, in-demand, and often better paid than general ultrasound technicians.
Can I take cardiac sonography programs online?
Yes, several online cardiac sonography programs exist, but they’re hybrid in nature. While lectures and coursework can be completed online, clinical training must still be done in-person at an approved hospital or diagnostic center. Online options are great for students balancing family or jobs, providing flexibility in scheduling. However, ensure the program is accredited, since only accredited schools qualify you to sit for certification exams like RDCS or RCS.
What certifications do cardiac sonographers need?
Most employers require certification to ensure quality and safety in patient care. The two most recognized credentials are: Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer (RDCS), offered by ARDMS, and Registered Cardiac Sonographer (RCS), offered by CCI. Completing accredited cardiac sonographer certification programs helps prepare for these exams. Certification proves your competence, increases job opportunities, boosts salary, and builds trust with patients and physicians who rely on accurate diagnostic images.
Is pediatric cardiac sonography a good career choice?
Yes, pediatric cardiac sonography is an excellent career for those passionate about working with children. Specialists in this field diagnose and monitor congenital heart defects in infants and kids. Training requires additional coursework and clinical rotations in pediatric hospitals. Salaries are often higher than general cardiac sonographers due to advanced expertise. Beyond pay, the role is deeply rewarding, as it allows you to make a difference in children’s lives.

