Choosing a career in medical imaging is a rewarding path, especially when it involves helping children with heart-related conditions. One of the specialized roles in this field is that of a pediatric cardiac sonographer, also known as a pediatric diagnostic medical sonographer. This career combines advanced ultrasound technology with compassionate patient care, allowing professionals to make a real difference in the lives of young patients and their families.
In this complete guide, we will explore the entry level pediatric cardiac sonographer salary, job outlook, education requirements, and career growth opportunities. Whether you’re just starting out or considering switching to this field, this article will give you the insights you need to make an informed decision.
What Does a Pediatric Cardiac Sonographer Do?
Before diving into salaries, it’s important to understand the role itself. A pediatric cardiac sonographer is a highly skilled healthcare professional who uses ultrasound equipment to evaluate the structure and function of a child’s heart.
Their responsibilities often include:
-
Performing echocardiograms on infants, children, and sometimes teenagers.
-
Assisting pediatric cardiologists in diagnosing congenital heart defects.
-
Maintaining detailed imaging records for treatment planning.
-
Providing emotional support to children and families during procedures.
Unlike a general pediatric ultrasound technician, this role requires specialized training in pediatric and cardiac imaging. The added expertise typically results in higher pay compared to more general sonography roles.
Entry-Level Pediatric Cardiac Sonographer Salary
One of the most common questions for new graduates is: How much does an entry-level pediatric cardiac sonographer earn?
While salaries vary by state, employer, and level of certification, here is a general breakdown:
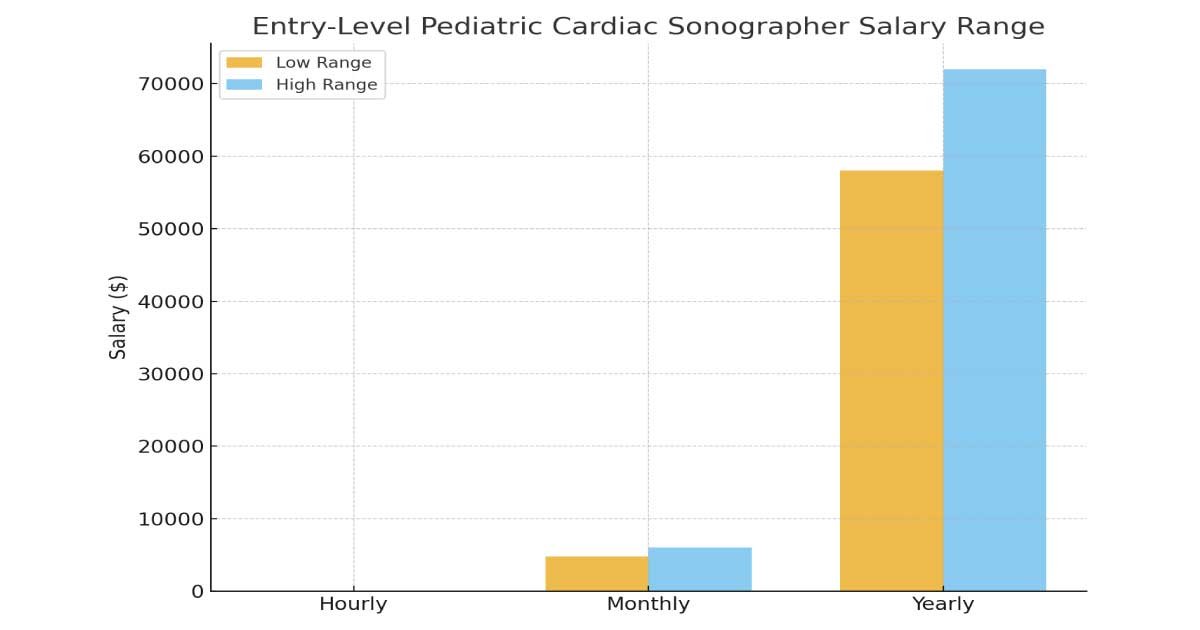
Hourly Pay: $28 – $35 per hour
Monthly Pay: $4,800 – $6,000 per month
Annual Pay: $58,000 – $72,000 per year
This range represents what newly certified professionals can expect in their first years on the job. Compared to other entry-level healthcare positions, the salary is competitive and offers room for steady growth as experience and certifications increase.
Factors That Influence Salary
Several factors affect how much an entry-level pediatric diagnostic medical sonographer earns:
Education and Training:
Graduates from accredited pediatric cardiac sonography programs often earn more than those who complete general sonography education. Employers value specialized training because it ensures competence in working with pediatric patients.
Certification:
Passing exams from organizations like the ARDMS pediatric sonography board can significantly boost starting salaries. Certified professionals are in higher demand, and many hospitals require these credentials before hiring.
Location:
Salaries are often higher in large metropolitan areas where the cost of living is higher. States like California, New York, and Massachusetts typically offer higher pay compared to rural areas.
Employer Type:
Pediatric hospitals, children’s specialty clinics, and academic medical centers often pay more than small community hospitals or outpatient imaging centers.
Education Path: How to Become a Pediatric Cardiac Sonographer
To enter this career, the right education and clinical experience are essential. Students typically follow one of two main pathways:
1. General Sonography + Pediatric Specialization
Many students begin with pediatric sonographer schooling through general diagnostic medical sonography programs. After gaining experience, they specialize in pediatric cardiac imaging by completing advanced courses or certificate programs.
2. Direct Pediatric Cardiac Sonography Programs
Some schools offer dedicated pediatric cardiac sonography programs, which focus specifically on imaging the hearts of infants and children. These programs prepare graduates to work directly in pediatric cardiology departments upon graduation.
Required Schooling and Training
Becoming a pediatric ultrasound technician requires completing accredited coursework and clinical training. Typical requirements include:
-
An associate degree or bachelor’s degree in diagnostic medical sonography.
-
Completion of pediatric cardiac sonographer schooling through classroom study and clinical rotations.
-
Training in pediatric anatomy, physiology, and echocardiography.
-
Hands-on experience with children in hospital or clinical settings.
Graduates are then eligible to sit for the ARDMS pediatric sonography certification exams, which validate their skills and knowledge in this specialty.
Certification and Licensing
Certification plays a critical role in salary levels and job opportunities. The most recognized certification is offered by the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS pediatric sonography). Passing these exams demonstrates that the professional meets national standards for quality imaging and patient care.
Key certifications include:
-
Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer (RDCS) with a pediatric echocardiography specialty.
-
Additional ARDMS certifications in related fields for expanded career opportunities.
While licensing varies by state, certification is almost always required by employers to ensure safe and accurate imaging.
Salary Growth Beyond Entry-Level
The entry-level salary is only the beginning. With additional experience, certifications, and specialization, a pediatric cardiac sonographer can increase earnings significantly.
Here’s what career progression may look like:
-
1–3 Years of Experience: $65,000 – $80,000 annually.
-
3–5 Years of Experience: $80,000 – $95,000 annually.
-
Senior Sonographers / Lead Technologists: $95,000 – $110,000+.
Advanced roles in management, education, or research may lead to even higher salaries.
Job Outlook for Pediatric Cardiac Sonographers
The demand for sonographers continues to grow across the U.S., and pediatric cardiac sonography is no exception. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects strong growth for diagnostic medical sonographers due to:
-
Rising rates of congenital heart disease detection.
-
Advances in non-invasive imaging technology.
-
A growing need for specialized pediatric healthcare services.
For entry-level professionals, this means stable employment opportunities and room for advancement.
Work Environment and Benefits
Entry-level pediatric cardiac sonographers often work in:
-
Children’s hospitals
-
Pediatric specialty clinics
-
University medical centers
-
Outpatient cardiology practices
In addition to salary, benefits typically include:
-
Health, dental, and vision insurance
-
Paid time off and sick leave
-
Retirement plan contributions
-
Tuition assistance for continuing education
The emotional rewards are also significant, as professionals play a key role in diagnosing and monitoring life-changing conditions for children and their families.
Challenges of Starting Out
While the career offers many rewards, entry-level professionals may face challenges, such as:
-
Adjusting to emotionally intense situations when working with sick children.
-
Mastering complex echocardiography techniques.
-
Managing the pressure of working alongside pediatric cardiologists who rely on accurate imaging.
Fortunately, strong training through pediatric sonography programs and mentorship during clinical rotations helps prepare new sonographers to handle these challenges with confidence.
Real-Life Perspective: First-Year Experiences
Many new graduates describe their first year as both exciting and demanding. Entry-level sonographers often emphasize the importance of mentorship from senior colleagues. They also highlight the joy of watching children grow healthier with the help of accurate diagnoses.
This combination of emotional fulfillment and competitive salary makes the field appealing for those who are passionate about pediatric healthcare.
Comparing Pediatric Cardiac Sonographer Salary with Other Specializations
To better understand the value of this career, it helps to compare salaries with other sonography fields. Entry-level general sonographers usually earn between $55,000 and $65,000 annually, while vascular or abdominal sonographers often start in a similar range.
However, pediatric cardiac sonographers typically start higher, with averages between $58,000 and $72,000. This is largely because of the specialized nature of the role and the additional pediatric sonographer schooling required. Unlike general programs, pediatric cardiac sonography programs include advanced training in echocardiography, child psychology, and congenital heart conditions.
In short, the added expertise makes you more valuable to hospitals and clinics, translating into better pay and job stability.
How Students Can Maximize Their Entry-Level Salary
If you are still in training or considering entering the field, there are steps you can take to boost your starting pay:
Choose Accredited Programs: Employers prefer graduates from accredited pediatric sonography programs because they meet strict education and clinical training standards.
Earn ARDMS Certification Early: Passing the ARDMS pediatric sonography exam before you start applying for jobs gives you a competitive edge. Many hospitals will pay certified candidates more from day one.
Gain Clinical Experience: During pediatric cardiac sonographer schooling, take every opportunity for hands-on training in children’s hospitals or pediatric cardiology departments. Employers value graduates who already have real-world experience.
Network with Professionals: Joining professional organizations and attending conferences helps you connect with hiring managers and mentors who can guide you toward higher-paying opportunities.
Career Advancement Opportunities
While entry-level salaries are solid, the real advantage of this career is growth potential. With experience, pediatric cardiac sonographers can transition into roles such as:
Lead Sonographer or Department Supervisor – managing teams and overseeing training.
Clinical Instructor – teaching in pediatric ultrasound technician programs or universities.
Research Specialist – working with cardiologists on new imaging techniques.
Travel Sonographer – moving between hospitals, often earning higher pay and travel stipends.
Each of these pathways comes with significant salary increases, sometimes exceeding $110,000 annually.
Why This Career is Worth It
Becoming a pediatric diagnostic medical sonographer requires commitment, but the rewards are unique. Not only do you earn a competitive income, but you also become a vital part of a child’s healthcare journey. Every scan you perform provides doctors with critical information to treat heart conditions early, giving young patients the chance for healthier, brighter futures.
This mix of financial stability, professional growth, and emotional fulfillment makes pediatric cardiac sonography one of the most rewarding specialties in medical imaging.
Conclusion
An entry-level pediatric cardiac sonographer salary offers a strong start in the healthcare field, with earnings ranging from $58,000 to $72,000 per year. While pay varies depending on location, certification, and employer, the long-term growth potential is excellent.
By completing accredited pediatric cardiac sonography programs or pediatric sonographer schooling, and obtaining ARDMS pediatric sonography certification, new graduates can secure stable and rewarding careers. Beyond financial rewards, the role provides a unique opportunity to make a lasting difference in the lives of children with heart conditions.
For anyone considering a path in sonography, specializing as a pediatric diagnostic medical sonographer is both a meaningful and financially promising choice.
💎 👉 To understand sonographer pay trends, visit Sonographer Salary. Discover hourly, monthly, and annual wages for professionals by specialization, location, and career stage. Accurate insights for USA ultrasound jobs with growth outlook included.
FAQs:
What is the average entry-level pediatric cardiac sonographer salary in the U.S.?
Entry-level pediatric cardiac sonographers typically earn between $58,000 and $72,000 annually. Pay varies by location, certification, and type of employer. Graduates from accredited pediatric cardiac sonography programs and those holding ARDMS pediatric sonography certification often secure higher starting salaries. Large children’s hospitals and specialty clinics usually offer more competitive pay compared to small outpatient centers.
Do I need certification to work as a pediatric cardiac sonographer?
Yes. Most employers require certification from the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS). The ARDMS pediatric sonography exam validates your skills in pediatric echocardiography and improves your job prospects. Certified sonographers often earn more and have access to better career opportunities. Certification demonstrates commitment, professionalism, and technical competence, making it essential for long-term success in the field.
What type of schooling is required to become a pediatric cardiac sonographer?
Students must complete accredited pediatric sonographer schooling or general diagnostic medical sonography programs with a pediatric cardiac specialization. Coursework typically includes anatomy, physiology, echocardiography, and pediatric imaging. Clinical rotations provide hands-on training in hospitals. Some schools offer direct pediatric cardiac sonography programs, while others prepare students to specialize after general training. An associate or bachelor’s degree is usually required for certification eligibility.
How long does it take to complete pediatric sonography programs?
Most pediatric sonography programs take two to four years, depending on whether you pursue an associate or bachelor’s degree. Some accelerated certificate programs may take 12–18 months for students with prior healthcare experience. After graduation, additional months may be needed to prepare for the ARDMS pediatric sonography exam. Completing schooling and certification typically takes around three years in total.
What is the difference between a pediatric ultrasound technician and a pediatric cardiac sonographer?
A pediatric ultrasound technician performs general imaging on children, such as abdominal or musculoskeletal scans. A pediatric cardiac sonographer, however, specializes in echocardiograms that focus on heart structure and function. Because of this specialized training, pediatric cardiac sonographers typically complete advanced pediatric cardiac sonographer schooling and earn higher salaries compared to general pediatric ultrasound technicians.
Can entry-level pediatric cardiac sonographers advance in their careers?
Absolutely. Entry-level professionals can move into senior roles, management, or teaching positions with experience. Many become lead sonographers, clinical instructors, or researchers. Some even work as travel sonographers, earning higher pay and benefits. Continued education, advanced certifications, and experience in specialized pediatric cardiology departments greatly expand career opportunities and salary growth for a pediatric diagnostic medical sonographer.
Are pediatric cardiac sonographers in demand?
Yes. The demand for skilled pediatric cardiac sonographers is growing as technology advances and more children require non-invasive heart imaging. Hospitals and pediatric cardiology clinics rely heavily on specialists trained in pediatric cardiac sonography programs. Job stability is excellent, and certified professionals often receive multiple job offers after graduation, especially in metropolitan areas with large children’s hospitals.