In the world of healthcare, there are many critical roles that work behind the scenes to diagnose, treat, and monitor patient conditions.
One such specialized role is that of an Echocardiography Technologist, also known commonly as a Cardiac Sonographer.
These professionals play a vital part in cardiac care through imaging technologies that allow physicians to visualize the heart in real time.
In this blog post, we will dive into what an echocardiography technologist does, the education and certification requirements,
salary expectations, job outlook, key skills needed, day‑to‑day responsibilities, and tips for building a successful career in this field.
What Is an Echocardiography Technologist?
An Echocardiography Technologist is a healthcare professional trained to perform diagnostic imaging procedures using ultrasound technology to produce images of the heart.
These images help doctors assess heart structure and function, identify diseases, and monitor treatment outcomes.
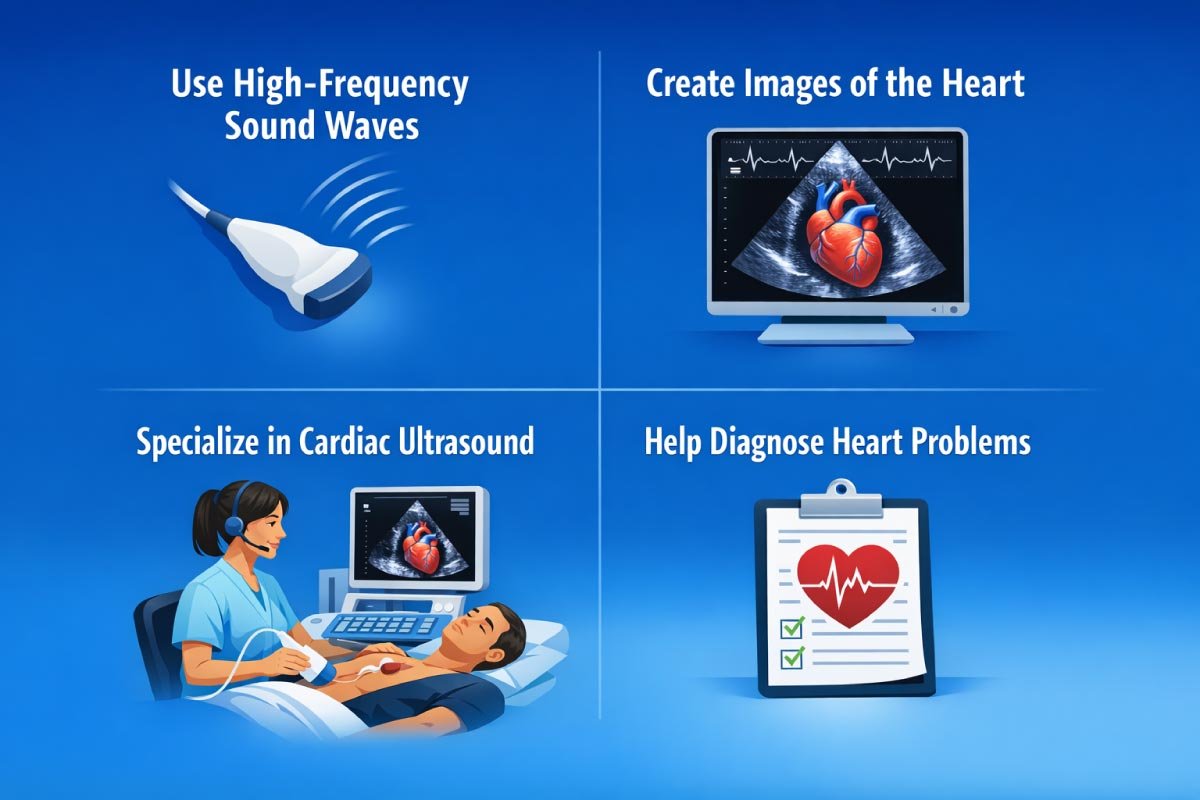
Unlike other imaging specialists (such as radiology techs who may image multiple body parts), echocardiography techs specialize specifically in cardiac ultrasound — often referred to as echocardiography.
In simpler terms:
They use high‑frequency sound waves to “look inside” the heart and create images that help diagnose heart problems.
Why Echocardiography Matters in Healthcare
Echocardiography plays a vital role in modern medicine by providing real-time, non-invasive imaging of the heart.
It helps healthcare professionals assess cardiac structure, blood flow, and function, supporting accurate diagnosis, timely intervention, and improved patient outcomes across diverse clinical settings.
Key Benefits of Echocardiography
Echocardiography offers a safe, reliable, and highly effective method for evaluating heart health.
Using sound waves, it provides detailed insights into cardiac structure and performance, helping physicians make confident clinical decisions while minimizing patient risk and discomfort.
-
Non‑invasive: No cutting, needles, or radiation — safer for repeated use.
-
Real‑Time Imaging: Shows heart motion and blood flow as it happens.
-
Diagnostic Precision: Helps detect valve issues, congenital defects, blood clots, and more.
-
Widely Accessible: Performed in hospitals, clinics, outpatient centers, and mobile units.
Because of this importance, technologists in this field are in demand and respected for their expertise.
Day‑to‑Day Responsibilities
Day-to-day responsibilities of an echocardiography technologist involve a balance of technical precision and compassionate patient care.
From preparing patients to capturing accurate cardiac images, these professionals play a vital role in supporting diagnosis, ensuring safety, and assisting cardiologists throughout daily clinical operations.
Typical Tasks
| Task Category | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Patient Interaction | Prepare patients, review history, explain the procedure, answer questions |
| Imaging Procedures | Perform transthoracic, stress, and sometimes transesophageal echocardiograms |
| Equipment Management | Adjust ultrasound machines, monitor quality, troubleshoot |
| Data Documentation | Save, label, and transfer images to physicians |
| Collaboration | Work with cardiologists, nurses, and other team members |
| Safety Protocols | Follow infection control, patient safety guidelines |
Successful techs blend both technical expertise and patient care skills in their routine.
Education and Training Path
Pursuing a career in echocardiography requires a structured educational journey that builds both scientific knowledge and hands-on clinical skills.
Through accredited programs and supervised training, students learn cardiac anatomy, ultrasound physics, patient care, and imaging techniques essential for professional competency.
Typical Education Pathway
The education pathway for echocardiography technologists combines academic learning with hands-on clinical training.
From building a strong science foundation in high school to completing specialized degree programs and certification preparation,
each stage equips students with the knowledge and skills needed for professional practice in cardiac imaging.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| High School | Focus on sciences: biology, physics, math |
| Associate Degree | 2‑year program in cardiovascular technology or related field |
| Bachelor’s Degree (Optional) | 4‑year degree for advanced knowledge and opportunities |
| Clinical Practicum | Hands‑on experience in a hospital or clinic |
| Certification Prep | Study for credentialing exams |
Most employers require at least an Associate Degree in diagnostic medical sonography or cardiovascular technology with an echocardiography focus.
Certifications and Licensing
Professional certification validates an echocardiography technologist’s knowledge, skills, and commitment to quality patient care.
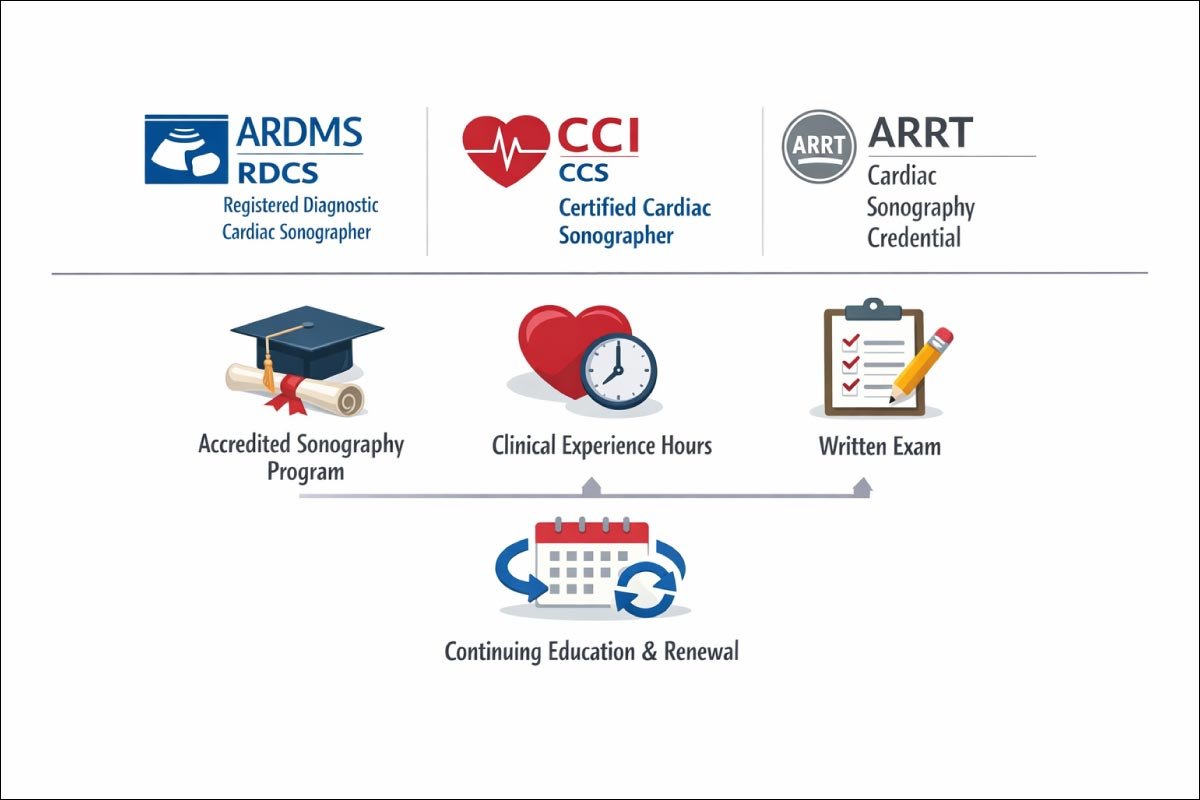
Earning recognized credentials enhances credibility, improves job prospects, and supports career growth by demonstrating compliance with industry standards and clinical excellence.
Major Certifying Bodies
Professional certification validates the skills and competence of echocardiography technologists.
Several recognized organizations offer credentials that demonstrate expertise in cardiac imaging.
Earning certification not only enhances credibility but also improves employment prospects, career advancement opportunities, and professional recognition within the cardiovascular healthcare field.
| Certifying Organization | Certification Offered |
|---|---|
| American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) | RDCS — Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer |
| Cardiovascular Credentialing International (CCI) | CCS — Certified Cardiac Sonographer |
| American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) | Cardiac Sonography Credential |
Each certification has eligibility requirements, typically involving:
-
Completion of an accredited sonography program
-
Clinical experience hours
-
Passing a written exam
Certifications often need renewal every few years through continuing education.
Salary Expectations & Job Outlook
Echocardiography technologists benefit from competitive compensation and strong employment prospects within the healthcare sector.
Growing cardiovascular care needs, aging populations, and advances in diagnostic imaging continue to drive demand, making this profession both financially rewarding and professionally stable.
Average Salary Ranges
Salary potential for echocardiography technologists increases with experience, specialization, and workplace setting.
Compensation varies widely based on geographic location, certifications, and advanced skills.
Understanding typical salary ranges helps professionals evaluate career growth, financial expectations, and long-term earning opportunities within the cardiac imaging field.
| Experience Level | Estimated Salary (USD) |
|---|---|
| Entry‑Level (0‑2 yrs) | $55,000 – $70,000 |
| Mid‑Career (3‑7 yrs) | $70,000 – $85,000 |
| Senior (8+ yrs) | $85,000 – $105,000+ |
| Specialized/Advanced Roles | $90,000 – $115,000+ |
Note: Salaries differ significantly depending on region, specialty skills, shift differentials, and benefits.
Job Outlook (10‑Year Growth)
The long-term employment outlook for echocardiography technologists remains highly positive.
Advances in cardiac care, preventive screening, and imaging technology are expanding the need for skilled professionals capable of supporting early diagnosis,
ongoing monitoring, and efficient treatment planning across diverse healthcare environments.
-
Aging populations
-
Increased cardiovascular screening
-
Preference for non‑invasive diagnostics
(Exact statistics vary by region and year; always consult your country’s labor data for the most current projections.)
Discover More:
Skills and Qualities of a Great Tech
Excelling as an echocardiography technologist requires a combination of technical expertise and interpersonal strengths.
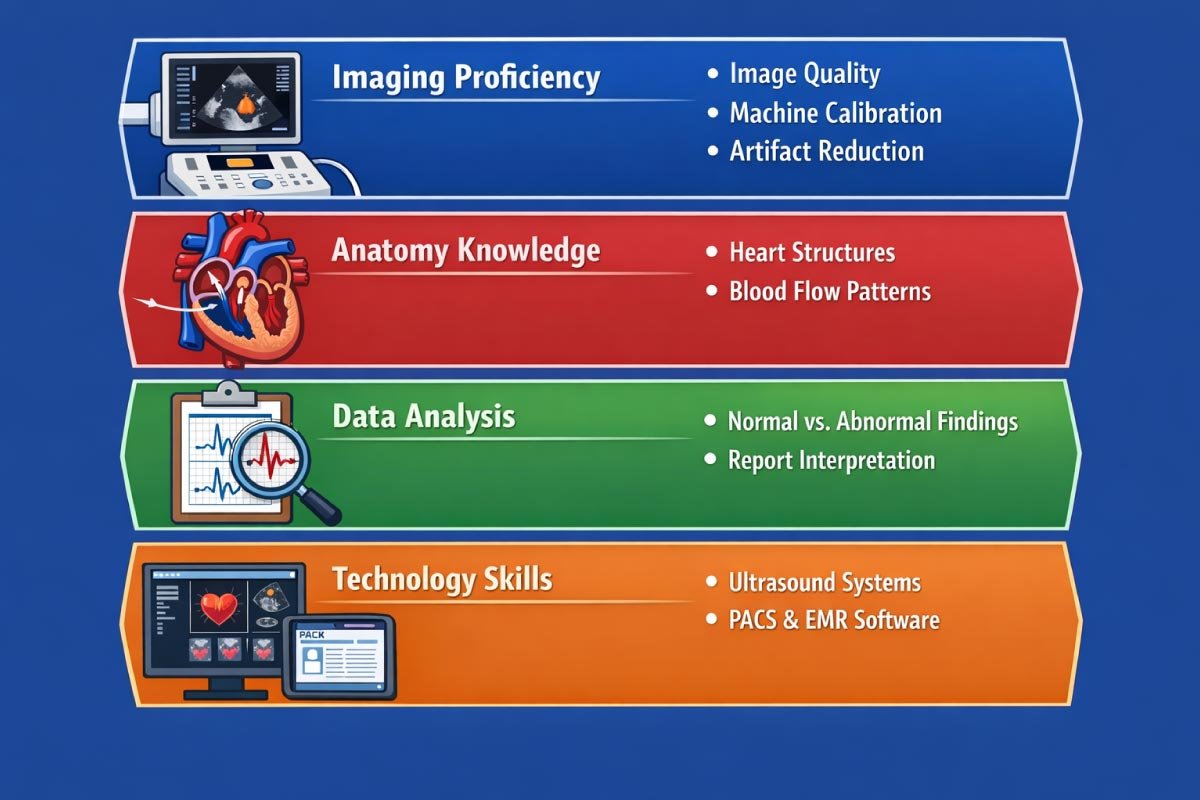
Mastery of imaging equipment, attention to detail, and critical thinking must be paired with communication, empathy, and adaptability to provide accurate diagnostics while ensuring a positive patient experience.
1- Core Technical Skills
Core technical skills are essential for echocardiography technologists to produce accurate, high-quality cardiac images.
Mastery of imaging techniques, heart anatomy, data analysis, and medical technology ensures reliable results.
These competencies enable technologists to support cardiologists effectively and contribute to precise diagnosis and optimal patient care.
| Skill Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Imaging Proficiency | Image quality, machine calibration, artifact reduction |
| Anatomy Knowledge | Heart structures, blood flow patterns |
| Data Analysis | Interpret and recognize normal vs abnormal findings |
| Technology Skills | Ultrasound systems, PACS, EMR software |
2- Essential Soft Skills
Essential soft skills complement technical expertise for echocardiography technologists.
Strong communication, empathy, accuracy, and teamwork enable them to guide patients, collaborate effectively with medical staff, and ensure precise documentation.
These interpersonal abilities enhance patient comfort and contribute to the overall quality and efficiency of cardiac imaging services.
| Soft Skill | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Communication | Explaining procedures, calming anxious patients |
| Empathy | Supporting patients during stressful exams |
| Accuracy | Precise labeling and documentation |
| Teamwork | Coordinating with medical staff |
Together, these help technologists provide high‑quality imaging and improve patient experience.
Discover More:
Career Advancement and Specialization
Echocardiography technologists have opportunities to expand their expertise and advance their careers through specialized training, certifications, and leadership roles.
Options include focusing on pediatric or adult echocardiography, vascular imaging, or supervisory positions,
allowing professionals to enhance their skills, increase earning potential, and contribute more broadly to patient care.
Possible Career Advancements
Echocardiography technologists have diverse opportunities for career advancement. Roles range from lead sonographer and clinical educator to equipment specialist or management positions.
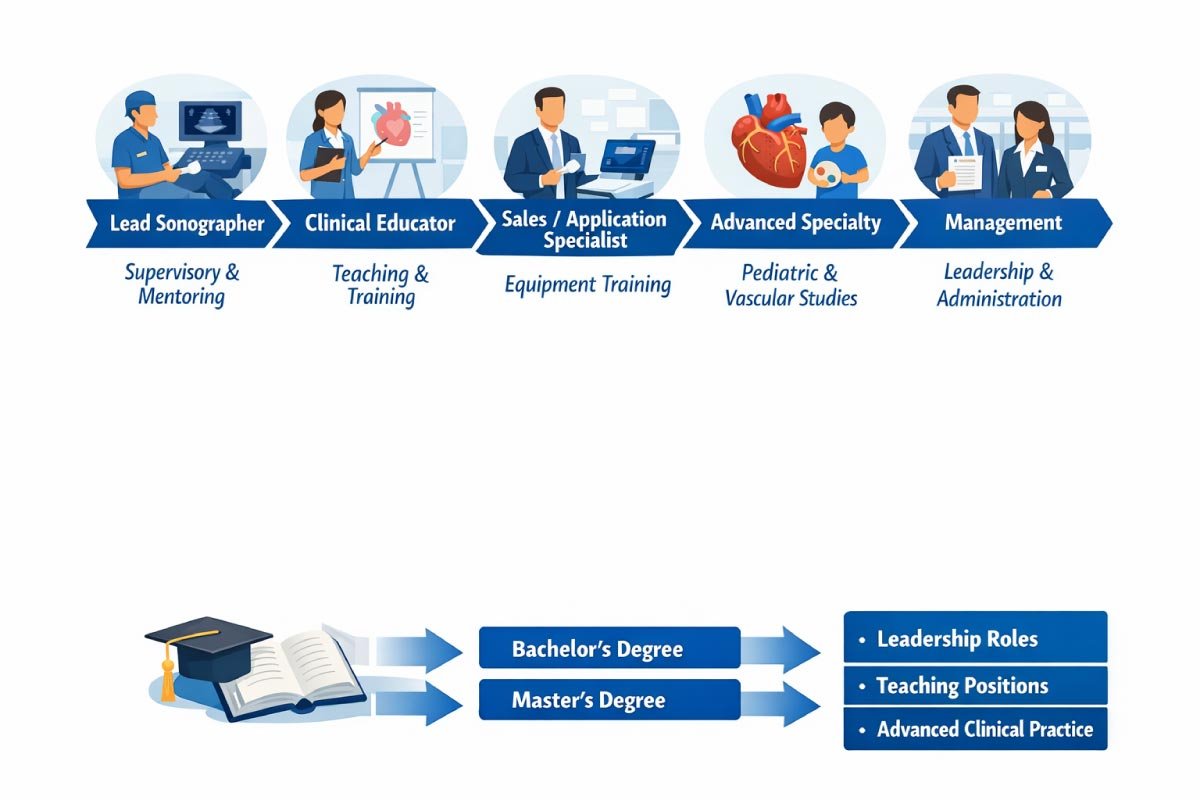
Pursuing further education or specialized training can open doors to leadership, teaching, research, or advanced clinical practice, allowing professionals to expand their impact within cardiovascular healthcare.
| Career Path | Description |
|---|---|
| Lead Sonographer | Supervisory role, mentoring junior techs |
| Clinical Educator | Teach in academic programs |
| Sales or Application Specialist | Training clinicians on imaging equipment |
| Advanced Specialty | Pediatric echo, vascular studies, research roles |
| Management | Department leadership, administration |
Some choose further education (e.g., Bachelor’s or Master’s degrees) to move into leadership, teaching, or advanced clinical roles.
Discover More:
Final Thoughts
Becoming an Echocardiography Technologist offers a rewarding blend of healthcare, technology, and direct patient impact.
With a path that includes structured education, valuable certifications, and opportunities for specialization, it’s a strong career choice for those passionate about cardiac care and medical imaging.

Zak is a dedicated medical and career writer specializing in sonography, healthcare education, and professional development. Through SonographerSalary.com, he shares in-depth insights on sonographer salaries, education pathways, and career tips to help readers build successful futures in medical imaging. His content combines accuracy with practical, easy-to-understand guidance, empowering students and professionals to make confident, informed career decisions.

