Ultrasound technology is a cornerstone of modern medical imaging. From diagnosing heart conditions to monitoring pregnancy, these machines provide critical, non-invasive insights into the human body. However, ultrasound systems come in many sizes and configurations, and choosing the right one can be challenging.
Understanding the ultrasound machine size, portability, and clinical application is key to ensuring effective imaging, workflow efficiency, and patient care.
This guide covers everything you need to know about ultrasound machine sizes, including portable, cart-based, and handheld systems, along with their benefits, limitations, and clinical applications.
What Is an Ultrasound Machine?
An ultrasound machine is a vital diagnostic tool used in medicine to visualize the body’s internal structures. By sending high-frequency sound waves into the body, it creates real-time images of organs, tissues, and blood flow.
These images help physicians diagnose conditions, guide procedures, and monitor patient health safely and non-invasively.
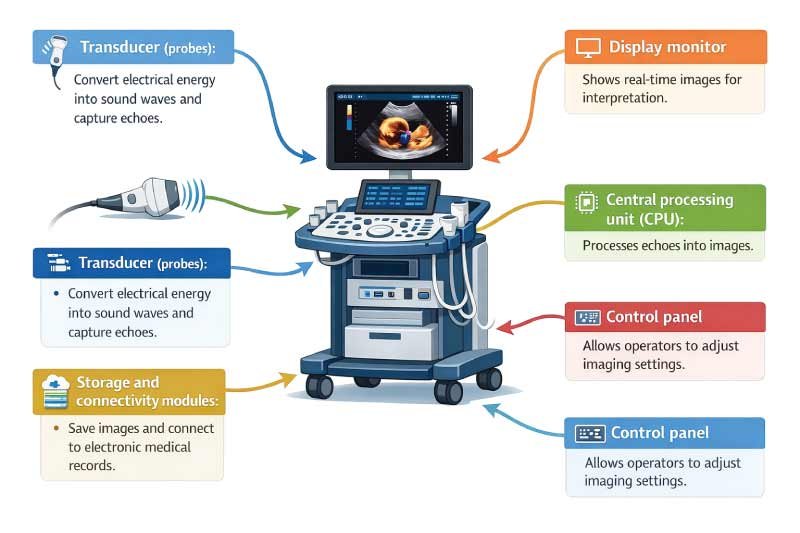
Transducers (probes): Convert electrical energy into sound waves and capture echoes.
Central processing unit (CPU): Processes echoes into images.
Display monitor: Shows real-time images for interpretation.
Control panel: Allows operators to adjust imaging settings.
Storage and connectivity modules: Save images and connect to electronic medical records.
Ultrasound machines vary widely in size, weight, and portability, making the selection process important for hospitals, clinics, and mobile services.
Factors Affecting Ultrasound Machine Size
Selecting the right ultrasound machine involves more than just price or brand. Factors like the type of clinical use, patient population, portability requirements, budget, and available space all influence the size and features needed.
Making an informed choice ensures accurate imaging, efficiency, and suitability for the healthcare setting.
Clinical Use: Imaging needs for cardiology, obstetrics, musculoskeletal, or emergency medicine differ.
Patient Population: Pediatric, neonatal, and adult patients may require different imaging capabilities.
Portability: Some settings require mobile machines or handheld devices.
Budget: Larger, full-featured systems are more expensive than compact or handheld models.
Space Availability: Small clinics may prefer compact or portable machines, while hospitals may accommodate cart-based systems.
Types of Ultrasound Machines by Size
Ultrasound machines vary widely in size, features, and clinical applications. Selecting the right machine depends on workflow, portability, and diagnostic needs.
Machines are commonly divided into four main types—handheld, portable/compact, cart-based, and specialized high-end systems—each suited for specific medical environments and patient care requirements.
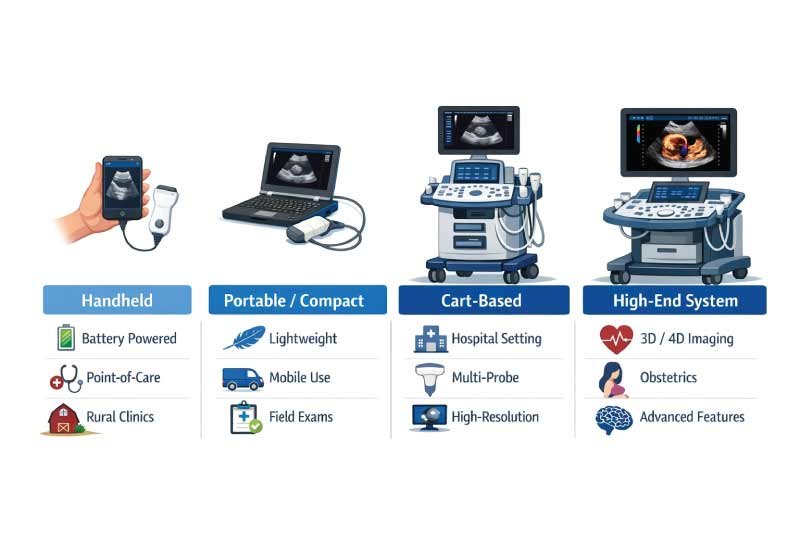
1. Handheld Ultrasound Machines
Handheld ultrasound machines are compact, lightweight, and designed for rapid bedside imaging. They are battery-operated and often connect to smartphones or tablets, making them ideal for point-of-care, emergency medicine, and rural clinics where portability and quick diagnostics are essential.
2. Portable / Compact Ultrasound Machines
Portable or compact machines weigh 5–15 kg and offer moderate imaging quality. They feature foldable screens and multiple probe support, making them suitable for bedside exams, mobile clinics, and fieldwork where mobility and general diagnostic capability are important.
3. Cart-Based Ultrasound Machines
Cart-based systems are full-size machines weighing 50–200 kg. They offer advanced imaging, multiple probe compatibility, and large displays. These machines are ideal for hospitals, specialty clinics, and full diagnostic imaging, providing high-resolution images for detailed patient evaluation.
4. Specialized High-End Ultrasound Systems
Specialized high-end systems are large, stationary machines ranging from 150–400 kg. They include 3D/4D imaging, cardiac modules, AI-assisted measurements, and advanced connectivity, making them suitable for cardiology, obstetrics, and research centers where precision and comprehensive imaging are critical.
| Machine Type | Size & Weight | Key Features | Typical Clinical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Handheld | Small, 0.5–2 kg | Pocket-sized, battery-operated, smartphone connectivity | Point-of-care, emergency medicine, rural clinics |
| Portable / Compact | 5–15 kg | Foldable screens, moderate imaging quality | Bedside exams, mobile clinics, fieldwork |
| Cart-Based | 50–200 kg | Full-size display, advanced features, multiple probes | Hospitals, specialty clinics, full diagnostic imaging |
| Specialized High-End Systems | 150–400 kg | 3D/4D imaging, cardiac modules, AI integration | Advanced cardiology, obstetrics, research centers |
Handheld Ultrasound Machines
Handheld ultrasound machines are compact, portable devices that fit in a pocket yet provide real-time imaging at the patient’s bedside. They are especially useful in emergency care, rural clinics, and home healthcare, offering quick assessments when traditional machines are impractical or unavailable.
Pros:
- Extremely portable
- Battery-operated, no need for wall power
- Affordable compared to full-size machines
Cons:
- Limited image resolution
- Fewer probe options
- Not suitable for detailed or complex studies
| Handheld Device Features | Typical Price Range | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Single probe, touchscreen | $2,000–$10,000 | Quick diagnostics, emergency medicine |
| Wireless connectivity | $5,000–$15,000 | Remote consultations, telemedicine |
| Battery life 2–4 hours | $2,500–$12,000 | Bedside point-of-care exams |
Portable / Compact Ultrasound Machines
Portable ultrasound machines offer a practical combination of mobility and reliable imaging, making them ideal for clinics, small hospitals, and mobile medical units.
They allow healthcare professionals to perform diagnostic scans efficiently without the need for large, stationary systems, while still supporting a variety of clinical applications.
Pros:
- Easy to move between rooms
- Good image quality for general diagnostics
- Multiple probes supported
Cons:
- Limited advanced features compared to cart-based systems
- Smaller screens than full-size machines
| Portable Ultrasound Features | Typical Size | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Foldable LCD display | 10–15 kg | Bedside abdominal scans, obstetric exams |
| Battery-operated | 5–8 hours | Mobile imaging services |
| Multiple transducer support | 10–12 kg | Cardiac, abdominal, vascular |
Cart-Based Ultrasound Machines
Cart-based ultrasound machines are full-size, stationary systems commonly used in hospitals and specialized clinics.
They offer advanced imaging capabilities, support multiple probes, and feature large displays, making them suitable for detailed diagnostics, research, and high-volume clinical applications where portability is not a priority.
Pros:
- Superior image resolution
- Supports multiple probes and advanced imaging modes (Doppler, 3D/4D)
- Large storage and connectivity options
Cons:
- Heavy and less portable
- Higher cost
- Requires more space
| Cart-Based Machine Features | Weight | Clinical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Large LCD/LED display | 100–200 kg | Cardiology, obstetrics, radiology |
| Multiple probe connectors | 150–180 kg | Abdominal, vascular, musculoskeletal |
| Advanced imaging software | 200 kg+ | Research and high-end diagnostics |
Also Read:
Specialized High-End Ultrasound Systems
Specialized high-end ultrasound systems are advanced imaging devices designed for cardiology, obstetrics, and research applications. They provide superior image quality, 3D/4D capabilities, and AI-assisted measurements, making them ideal for complex diagnostics and detailed studies.
Due to their size and sophistication, these systems are typically stationary and require trained operators.
| Feature | Description | Clinical Use |
|---|---|---|
| 3D/4D imaging | Real-time volumetric scans | Obstetrics, fetal anomaly detection |
| AI-assisted imaging | Automatic measurements | Cardiology, radiology, research |
| Multi-modal probes | Supports linear, convex, and phased array | Complex diagnostic studies |
Note: These systems are typically stationary due to size and weight, and require trained operators.
Choosing the Right Ultrasound Machine by Application
Selecting the right ultrasound machine depends on the clinical application, patient needs, and imaging complexity. Different specialties and care settings require specific features, from rapid bedside scans to advanced 3D/4D imaging.
Matching the machine to its intended use ensures accurate diagnostics, efficiency, and optimal patient care.
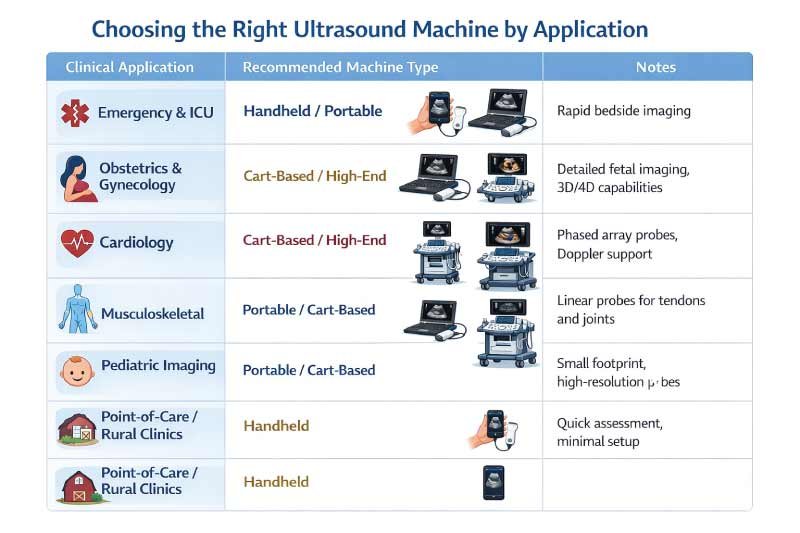
| Clinical Application | Recommended Machine Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency & ICU | Handheld / Portable | Rapid bedside imaging |
| Obstetrics & Gynecology | Cart-based / High-end | Detailed fetal imaging, 3D/4D capabilities |
| Cardiology | Cart-based / High-end | Phased array probes, Doppler support |
| Musculoskeletal | Portable / Cart-based | Linear probes for tendons and joints |
| Pediatric Imaging | Portable / Cart-based | Small footprint, high-resolution probes |
| Point-of-Care / Rural Clinics | Handheld | Quick assessment, minimal setup |
Advantages of Understanding Ultrasound Machine Sizes
Knowing the differences in ultrasound machine sizes helps healthcare providers choose the right system for their clinical needs.
Selecting an appropriately sized machine can enhance workflow, improve imaging quality, optimize costs, and increase patient comfort by providing efficient, bedside, and minimally disruptive diagnostics.
Improved Workflow: Selecting the right size ensures smooth patient throughput.
Better Imaging: Matching size to application improves diagnostic accuracy.
Cost Efficiency: Avoid overpaying for advanced features that aren’t needed.
Patient Comfort: Smaller, portable machines allow bedside imaging and reduce patient movement.
Also Read:
Ultrasound Machine Size and Portability Comparison
Understanding the size and portability of ultrasound machines helps clinics and hospitals choose the most suitable device for their workflow and budget. Comparing mobility, image quality, and cost ensures the right machine is selected for each clinical setting, from emergency care to specialized diagnostics.
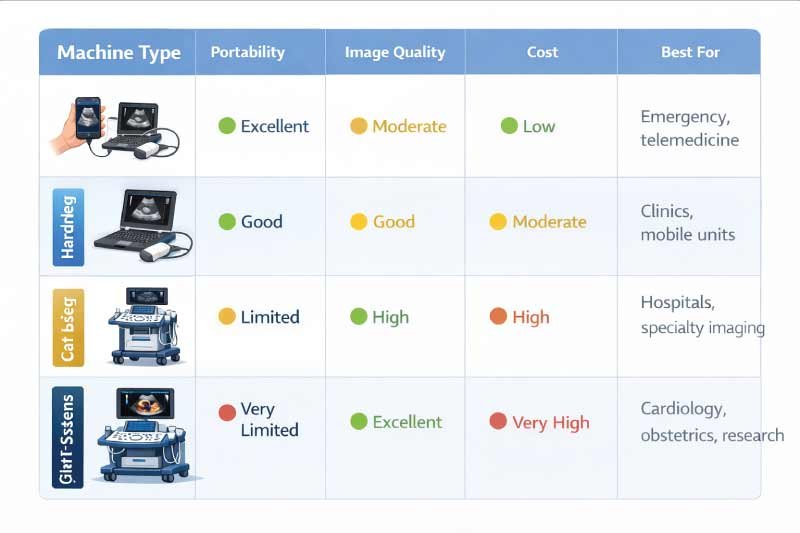
| Machine Type | Portability | Image Quality | Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Handheld | Excellent | Moderate | Low | Emergency, telemedicine |
| Portable | Good | Good | Moderate | Clinics, mobile units |
| Cart-Based | Limited | High | High | Hospitals, specialty imaging |
| High-End Systems | Very Limited | Excellent | Very High | Cardiology, obstetrics, research |
Future Trends in Ultrasound Machine Sizes
The future of ultrasound machines is moving toward compact, versatile, and smart systems. Advances in AI, wireless technology, and cloud integration are transforming how imaging is performed,
enabling clinicians to provide faster, more accurate, and remote diagnostics, while maintaining high-quality care beyond traditional hospital environments.
Handheld devices with AI assistance
Hybrid systems combining portability and advanced imaging
Wireless probe technology reducing the need for bulky consoles
Telemedicine integration for remote diagnostics
These innovations allow clinicians to deliver high-quality care outside traditional hospital settings.
Also Read:
Conclusion
Choosing the right ultrasound machine size is crucial for clinical efficiency, diagnostic accuracy, and patient care. Understanding the differences between handheld, portable, cart-based, and high-end systems ensures that healthcare providers select the optimal machine for their specific needs.
From emergency rooms to rural clinics and high-end cardiology departments, matching machine size to clinical application maximizes both workflow and imaging quality.
Pro Tip: Always evaluate your clinical needs, space availability, patient population, and budget before purchasing an ultrasound machine. Proper selection improves efficiency, patient comfort, and diagnostic confidence.
FAQs:
What Is Ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of the body’s internal organs, tissues, and blood flow. It is widely used because it is non-invasive, painless, and does not involve radiation, making it safe for repeated use.
Different Types of Ultrasound Machines?
There are several types of ultrasound machines, including handheld, portable, cart-based, and high-end systems. Each type differs in size, image quality, and features. The choice depends on clinical needs, portability requirements, budget, and whether basic or advanced diagnostic imaging is required.
What Is an Ultrasound Machine Called?
An ultrasound machine is commonly called an ultrasound scanner or sonography machine. In medical settings, it may also be referred to as a diagnostic ultrasound system. These terms describe devices used to produce images of internal body structures using sound waves.
Ultrasound Machines: How Do They Work?
Ultrasound machines work by sending sound waves into the body through a transducer. These waves bounce off internal organs and return as echoes. The machine processes these echoes and converts them into real-time images displayed on a monitor for clinical evaluation.
Ultrasound Machine Description?
An ultrasound machine is a medical imaging device consisting of a transducer, control panel, processor, and display screen. It generates real-time images by using sound waves instead of radiation. Ultrasound machines are used in many specialties, including cardiology, obstetrics, and emergency medicine.
What is Ultrasound Machine Definition?
An ultrasound machine is defined as a diagnostic device that uses high-frequency sound waves to visualize internal body structures. It helps healthcare providers assess organs, tissues, blood flow, and fetal development. The technology is valued for its safety, accuracy, and ability to provide instant imaging results.
Types of Ultrasound Machine?
Types of ultrasound machines include handheld devices for point-of-care use, portable systems for clinics, cart-based machines for hospitals, and specialized high-end systems for advanced imaging. Each type serves different medical environments and diagnostic needs, from basic examinations to complex clinical studies.
How Does an Ultrasound Machine Work?
An ultrasound machine works by converting electrical energy into sound waves through a probe. These waves travel into the body, reflect off tissues, and return to the probe. The system analyzes the returning signals to create detailed images used for diagnosis and monitoring.

Zak is a dedicated medical and career writer specializing in sonography, healthcare education, and professional development. Through SonographerSalary.com, he shares in-depth insights on sonographer salaries, education pathways, and career tips to help readers build successful futures in medical imaging. His content combines accuracy with practical, easy-to-understand guidance, empowering students and professionals to make confident, informed career decisions.