Medical imaging is a cornerstone of modern healthcare, enabling doctors to diagnose and monitor diseases with precision.
Among the professionals who make this possible are ultrasound technicians, also called diagnostic medical sonographers.
These experts use high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body, helping detect conditions ranging from pregnancy-related issues to cardiovascular diseases.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what an ultrasound technician does, how to become one, salary expectations, career growth opportunities, and the future outlook.
Whether you are just starting your healthcare journey or considering a career shift, this guide will provide the information you need.
Understanding the Role of an Ultrasound Technician
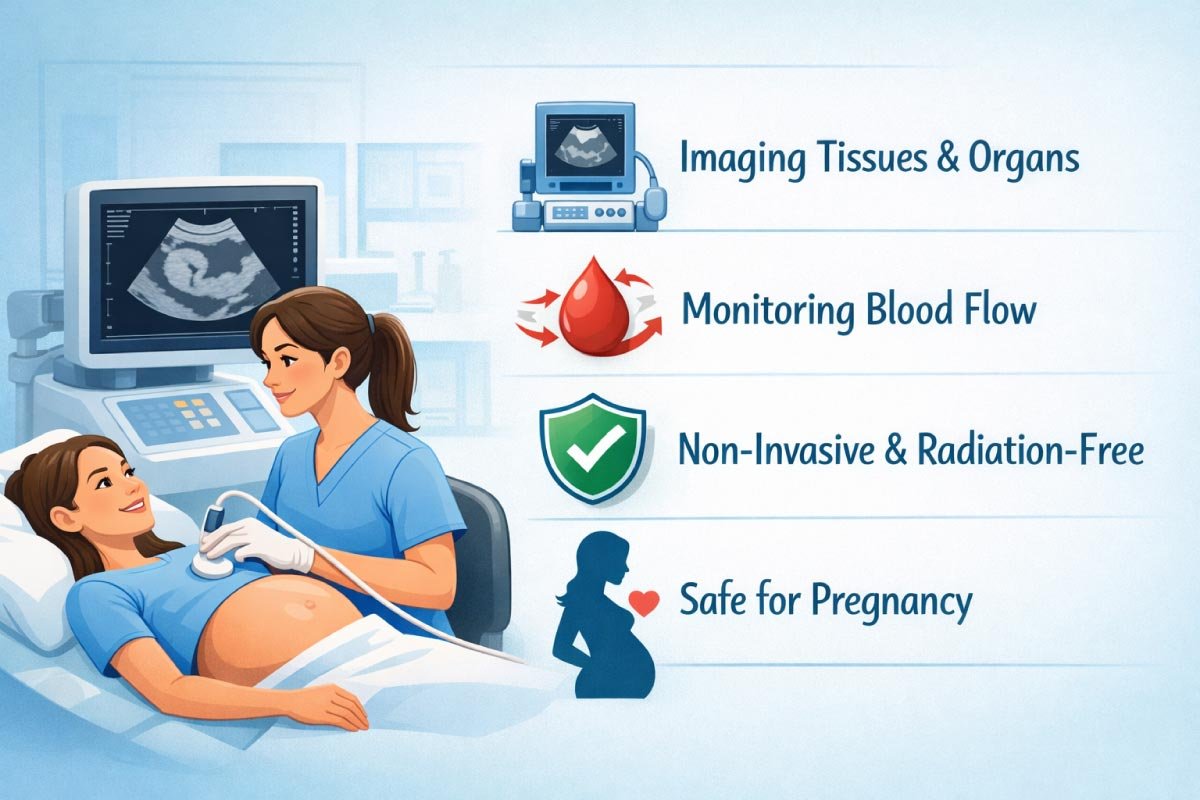
An ultrasound technician specializes in using ultrasound equipment to capture images of tissues, organs, and blood flow.
Unlike X-rays, ultrasounds are non-invasive and radiation-free, making them safer for repeated use, particularly for pregnant women.
Key Responsibilities
Ultrasound technicians play a vital role in medical imaging, ensuring accurate diagnostics and patient care.
Their responsibilities range from preparing patients and capturing high-quality images to assisting physicians and maintaining equipment.
Specialization in specific imaging areas can shape career opportunities, professional development, and compensation in this dynamic field.
| Responsibility | Description |
|---|---|
| Patient Preparation | Explain procedures, answer questions, and ensure patient comfort |
| Image Acquisition | Operate ultrasound equipment to capture clear images |
| Image Analysis | Review images for quality and preliminary findings |
| Documentation | Maintain accurate records for doctors and hospitals |
| Equipment Maintenance | Clean and calibrate machines regularly |
| Assisting Physicians | Help during image-guided procedures like biopsies |
Technicians often specialize in areas such as obstetrics, abdominal imaging, cardiovascular sonography, or musculoskeletal imaging.
This specialization may influence salary, career growth, and required certifications.
Education Requirements
Pursuing a career in sonography demands a solid educational background.
Prospective sonographers must complete specialized training that combines both theoretical knowledge and hands-on clinical experience.
Coursework typically covers anatomy, physiology, and imaging techniques, preparing students to meet industry standards and succeed in a professional setting.
Most employers require formal training from an accredited program.
Common Educational Paths
| Program | Duration | Overview |
|---|---|---|
| Certificate | 12–18 months | Covers basic ultrasound principles and clinical practice |
| Associate Degree | 2 years | Core medical sciences, hands-on clinical rotations |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 4 years | Advanced sonography techniques, leadership, research |
Programs accredited by CAAHEP (Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs) are preferred, as they prepare students for national certification exams. Clinical experience is essential to master patient handling, machine operation, and image interpretation.
Certifications and Licensing
Obtaining certification and licensure is an important step for sonographers seeking professional credibility.
Credentials demonstrate proficiency in imaging techniques, patient care, and safety standards.
Many employers prefer or require certified staff, as certification reflects a commitment to quality and expertise.
While certification isn’t mandatory in every region, it greatly enhances employment opportunities and earning potential.
Common Certifications
Ultrasound technicians can enhance their credentials through certifications such as RDMS, RCS, ARRT
Sonography, and BLS/CPR, each focusing on specialized skills or emergency preparedness.
Obtaining these certifications not only validates expertise but also may be required by employers,
or state regulations, ensuring safe, competent, and legally compliant practice in medical imaging.
| Certification | Focus Area | Certifying Body |
|---|---|---|
| RDMS | General sonography | ARDMS (American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography) |
| RCS | Cardiac sonography | CCI (Cardiovascular Credentialing International) |
| ARRT Sonography | Alternative credential | ARRT (American Registry of Radiologic Technologists) |
| BLS / CPR | Emergency preparedness | American Heart Association |
Many states in the U.S. also require licensure or registration to legally practice, so it’s important to check local regulations.
Salary Overview

Earnings for ultrasound technicians are influenced by factors such as geographic region, years of experience, and area of expertise.
Salary ranges can differ widely between hospitals, clinics, and private practices.
Understanding the compensation landscape helps aspiring sonographers make informed career decisions. Ultrasound technician salaries vary depending on location, experience, and specialization.
4.1 Salary by Experience in the U.S.
Ultrasound technician salaries in the U.S. vary with experience, ranging from around $60,000 for entry-level positions to over $100,000 for advanced or specialized roles.
Location also impacts earnings, with urban hospitals and specialized imaging centers generally offering higher compensation compared to smaller clinics or rural healthcare facilities.
| Experience Level | Average Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| Entry-Level (0–2 years) | $60,000 |
| Mid-Level (3–5 years) | $75,000 |
| Experienced (6–10 years) | $88,000 |
| Advanced/Specialized (10+ years) | $100,000+ |
Technicians working in urban hospitals or specialized imaging centers typically earn more than those in smaller clinics or rural areas.
4.2 Salary by Specialty
Ultrasound technician salaries also vary by specialty, with cardiovascular and vascular imaging typically earning the highest, while abdominal and obstetric imaging fall slightly lower.
Pursuing a specialty often requires extra certification but provides greater earning potential, career advancement, and opportunities for leadership within medical imaging departments.
| Specialty | Average Salary |
|---|---|
| Obstetric / Gynecologic | $78,000 |
| Cardiovascular | $85,000 |
| Musculoskeletal | $80,000 |
| Abdominal Imaging | $76,000 |
| Vascular | $88,000 |
Specialization requires additional certification but offers higher pay and opportunities for leadership roles.
Career Opportunities
A career as an ultrasound technician offers diverse opportunities across hospitals, clinics, and specialized imaging centers.
Professionals can advance into leadership, education, or niche areas such as cardiovascular or obstetric sonography.
Demand for skilled technicians continues to grow, driven by healthcare needs and innovation. Growth is fueled by an aging population, increasing medical imaging needs, and technological advances.
Potential Career Paths
| Role | Requirements |
|---|---|
| General Sonographer | Entry-level certification and degree |
| Lead Sonographer | Several years experience + specialty credential |
| Clinical Educator | Teaching or training experience |
| Department Supervisor | Leadership + advanced credentials |
| Private Practice Consultant | Specialization + extensive clinical expertise |
Expanding your skill set into multiple imaging modalities or administrative roles can significantly increase earning potential.
Discover More:
Job Outlook
The demand for ultrasound technicians is rising as healthcare services expand and medical imaging becomes increasingly essential.
Opportunities are expected to grow across hospitals, outpatient centers, and specialty clinics. This positive trend highlights the profession’s stability and potential for advancement.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that ultrasound technician employment will grow 17% from 2022 to 2032, much faster than the average for all occupations.
Factors Driving Growth
The ultrasound technician field is experiencing growth due to factors like an aging population, advances in portable,
and high-tech equipment, increased preventive care, and a preference for non-invasive imaging.
Demand is especially strong in specialized areas such as cardiovascular and fetal echocardiography, creating expanded opportunities for trained professionals.
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Aging Population | More diagnostic exams for heart, vascular, and abdominal conditions |
| Technology Advances | Portable and advanced ultrasound machines increasing demand |
| Preventive Care | Routine screenings in outpatient clinics and hospitals |
| Non-invasive Preference | Ultrasound preferred over radiation-based imaging |
Specialized fields like cardiovascular and fetal echocardiography are expected to see even stronger demand.
Work Environment
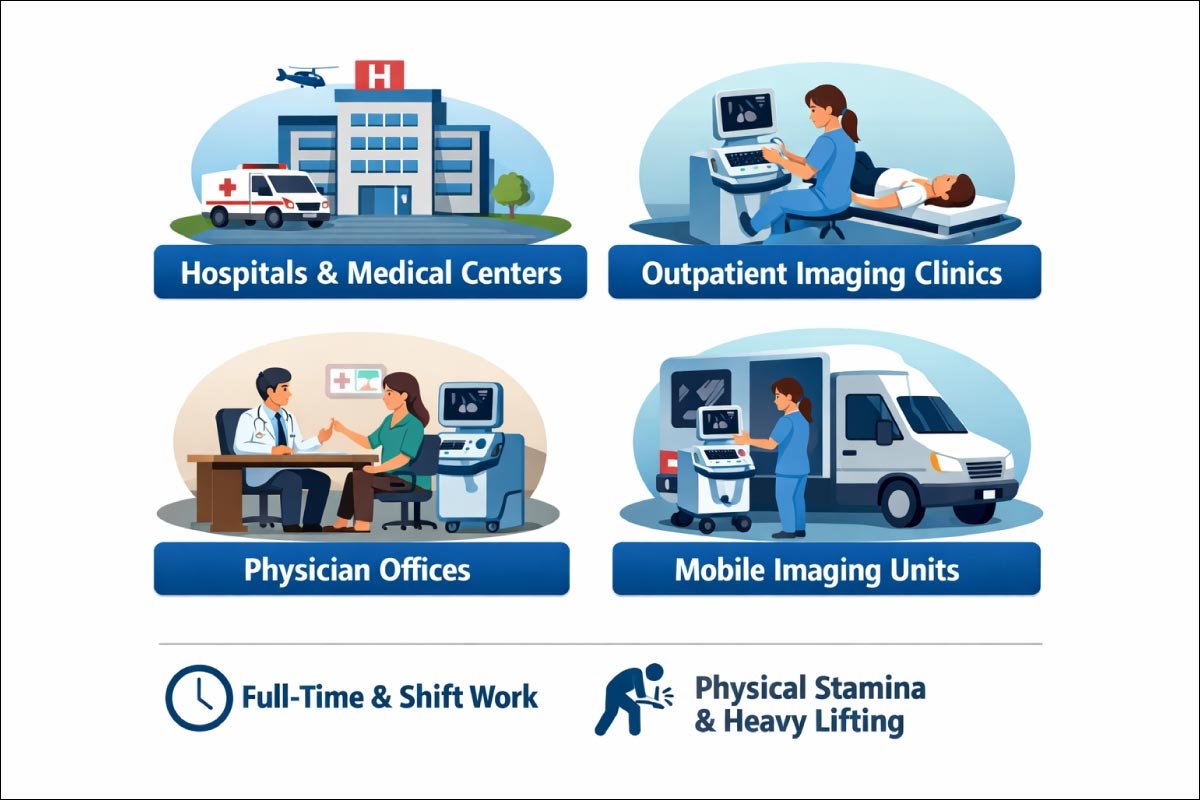
Ultrasound technicians operate in a variety of healthcare settings, interacting with patients and medical staff daily.
Their workspaces range from bustling hospitals to specialized clinics, requiring both technical skill and patient care abilities.
The role often demands physical endurance and adaptability.
-
Hospitals and medical centers
-
Outpatient imaging clinics
-
Physician offices
-
Mobile imaging units
Technicians typically work full-time, though some facilities offer part-time or shift-based schedules.
Physical stamina is essential as many procedures require standing and maneuvering equipment for long periods.
Discover More:
Pros and Cons of Being an Ultrasound Technician
Pros
| Pros | Details |
|---|---|
| High Job Demand | Strong employment growth and job stability |
| Meaningful Work | Direct impact on patient care and diagnostics |
| Variety | Multiple specialties and career paths |
| Technology | Hands-on experience with advanced medical equipment |
| Relatively Short Training | Compared to physicians or other healthcare professionals |
Cons
| Cons | Details |
|---|---|
| Physically Demanding | Long periods of standing and positioning patients |
| Irregular Hours | Some hospitals require nights or weekends |
| Emotional Challenges | Dealing with patients receiving bad news |
| Continuing Education | Certifications must be maintained and updated |
Tips to Succeed as an Ultrasound Technician
Excelling as an ultrasound technician requires a combination of formal education, hands-on experience, and continuous professional development.
Strategic choices in training, specialization, and skill-building can enhance career prospects, efficiency, and patient care.
Staying current with technological advances and cultivating strong interpersonal skills is essential for long-term success.
-
Choose Accredited Programs: Ensure your program is recognized by CAAHEP for certification eligibility.
-
Gain Clinical Experience: Internships or rotations provide practical skills and confidence.
-
Specialize Strategically: Consider specialties with high demand for higher pay and job security.
-
Develop Soft Skills: Patient communication, empathy, and attention to detail are critical.
-
Stay Updated: Medical imaging technology evolves rapidly, requiring ongoing learning.
Discover More:
Future of Ultrasound Technology Careers
The future is bright for ultrasound technicians. AI-assisted imaging, portable devices, and remote diagnostics are transforming the profession.
Technicians who adapt to new technologies, expand their skillset, and earn multiple certifications will have a competitive advantage.
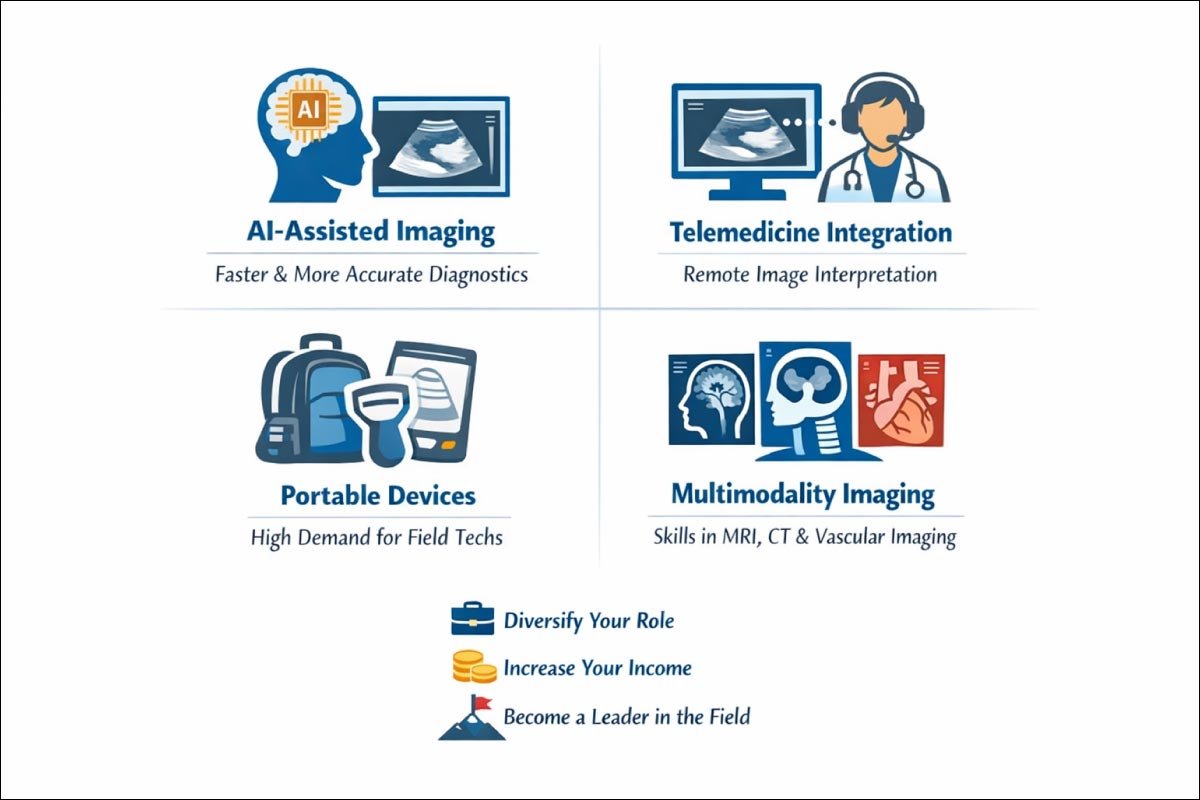
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in ultrasound technology, such as AI-assisted imaging, telemedicine integration, portable devices, and multimodality imaging, are transforming the profession.
Technicians who adopt these innovations can enhance diagnostic accuracy, expand their skill sets, work remotely,
and diversify their roles, ultimately boosting career opportunities, income, and leadership potential in the field.
| Trend | Impact |
|---|---|
| AI-assisted Imaging | Faster and more accurate diagnostics |
| Telemedicine Integration | Remote interpretation of images |
| Portable Devices | Increased demand for field technicians |
| Multimodality Imaging | Expanding skills into MRI, CT, and vascular imaging |
Ultrasound technicians who embrace these trends can diversify their roles, increase their income, and become leaders in the field.
Conclusion
An ultrasound technician career offers job stability, competitive salary, and the satisfaction of helping patients daily.
The field combines healthcare, technology, and patient interaction, providing a meaningful and dynamic career path.
With proper education, certification, and continuous skill development, ultrasound technicians can enjoy a rewarding profession with multiple growth opportunities.
Discover More:

Zak is a dedicated medical and career writer specializing in sonography, healthcare education, and professional development. Through SonographerSalary.com, he shares in-depth insights on sonographer salaries, education pathways, and career tips to help readers build successful futures in medical imaging. His content combines accuracy with practical, easy-to-understand guidance, empowering students and professionals to make confident, informed career decisions.

